low end tidal co2 after intubation
The end-tidal CO2 in these people will be unnaturally low. In patients with high risk for reintubation failure of two or more SBTs CHF CO2 greater than 45 after extubation weak cough pneumonia as a cause of respiratory failure the use of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation after extubation as a bridge to ventilator free-breathing has been shown to reduce ICU mortality and lower risk of intubation.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation.

. The new American Heart Association guidelines require secondary confirmation of proper tube placement in all patients by exhaled CO2 immediately after intubation and during transport. Attach End-Tidal CO2 detector to the Blind Insertion Airway Device or the Endotracheal Tube. End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2.
If confirmed in human beings this may prove to be a quick reliable method of detecting esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. EtCO2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of CO2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the alveolar CO2 concentration.
This article covers the terminology the basic physiology the technology both colorimetric detectors and infrared capnometers and the clinical applications of ETCO2 monitoring with special. Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values. Misting increased SaO2 Types of End-Tidal CO2 Qualitative Yes or No.
The objectives were 1 to establish immediately upon arrival to the emergency department ED the prevalence of abnormal end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 levels in patients with prehospital intubation and 2 to describe the relationship between abnormal ETCO2 levels on ED arrival and mortality. End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest. In group B ETCO2 ranged from 2 to 11 mm Hg median 3 mm Hg.
Over the ensuing minute the patients oxygen saturation declined from 93 to 82 and the end-tidal carbon dioxide decreased to 10 mm Hg. 9 Similar studies demonstrated an association of low Et co 2 values with mortality in various trauma groups but none identified a threshold value below which resuscitative efforts may be. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage.
The higher the ETCO2 measured during compressions the better the perfusion. A study of blunt trauma patients intubated in the prehospital settings demonstrated that Et co 2 after intubation was associated with 95 in-hospital mortality. Breath sounds were distant after the second intubation.
The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2 first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s.
The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide. Waveform capnography should be monitored in all intubated patients and displayed on the monitor as above.
The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg. A low end-tidal CO 2 in hypothermia. What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2.
After 20 minutes of CPR an end-tidal CO2 level of 19 mm Hg or less is predictive of death as an outcome of the cardiac arrest. Persistently low end-tidal CO2 check quality of compressions check. In this experimental model measurement of ETCO2 reliably distinguished esophageal from tracheal intubation during cardiac arrest and CCM.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. From the time of the esophageal extubation until the next intubation the patient was not ventilated by mask. This disposable bedside detector registers three ranges of CO2 concentration.
Its main use has been in verifying endotracheal tube position during mechanical ventilation and cardiopulmonary resuscitation but it is being studied and used for other purposes as well. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45. A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation.
The End-Tidal CO2 detector shall be used with any Endotracheal Tube or Blind Insertion Airway Device use. End-tidal carbon dioxide reflects CO 2 concentration of alveoli emptying last. In hypothermia the total body CO 2 production is greatly decreased as the metabolic rate is decreased by 6 for every degree below 36.
428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. This maximum concentration is called end-tidal carbon dioxide concentration or tension depending on whether it is expressed in fractional concentration or mm Hg.
The purposes of this study were to evaluate the clinical utility of a colorimetric end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detector in confirming proper endotracheal intubation in patients requiring emergency intubation to determine if this new device can be used as an adjunct to judge the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and to determine whether the device can predict. End-tidal CO2 monitoring is an exciting non-invasive technology that is more commonly used in the emergency department intensive care unit and in the prehospital setting. Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
Capno 101 How Does Capnography Work Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Ventilator Waveform Troubleshooting High Peak Pressures This

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
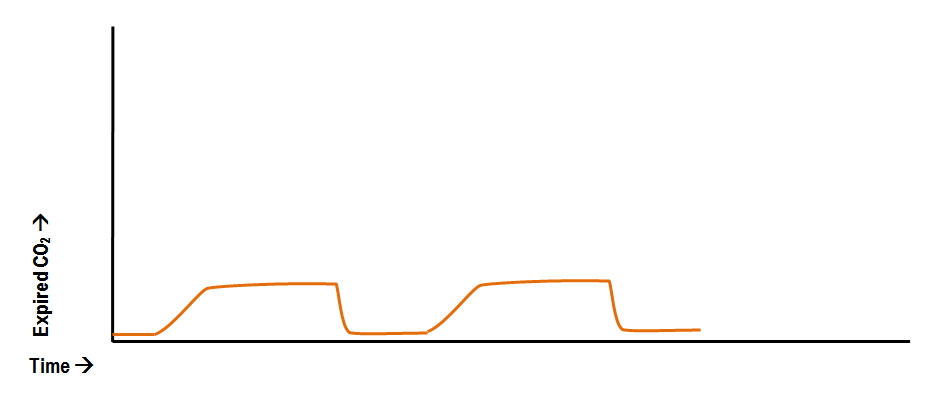
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology


